- Windows Storage Server 2012 Iso
- Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard
- Windows Server 2012 Free Download
Windows Storage Server 2012 delivers excellent economics for a shared storage solution by leveraging industry standard hardware matched with robust storage capabilities. It delivers continuous availability that is designed to protect from a range of failures and prevent downtime in a scalable and reliable manner. Configure Storage Space in Server 2012. To configure storage space, Storage Services server role must be installed. This server role is installed by default in Server 2012. As you can see below, I have two new physical disks, disk 1 and disk 2. We will combine these two disks and create some storage pools.
'Is there a default password for Windows server 2012 r2?' This is a question asked naturally because there is one default administrator in previous Windows operational systems. But there is one in server 2012 r2 the same?
From the installation of Windows server 2012 r2 essentials, we should remember an administrator password is asked to be set, otherwise we couldn't finish this operational system installation. Actually, it is default administrator built in Windows system, the password we set is default password used to login server before we create user account.
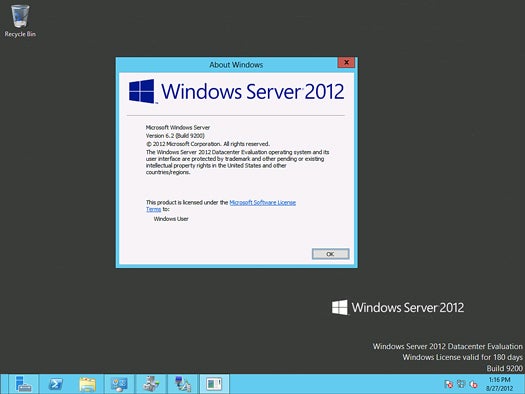
If we are careful in other Windows operational system installation process, we should know that built-in administrator is not asked to set default password. So even though when you forget user logon password in these Windows systems, you also could login into Windows with default administrator, as long as the built-in administrator has been enabled. But it's not the same for Windows server 2012 R2. Default administrator and password had better be saved in safe place.
Having said so much about whether there is default password in Windows server 2012 r2, what does it can do for us or server computer actually?
According to operation experience in other Windows system, we may realize lots of programs have to be run with admin privileges. However, it is always ignored even forgotten by computer users because they run computer and programs usually with other local administrator user accounts becaus of system and data security problem.
But, in a word, Windows server 2012 r2 default administrator and password still could help us to do:
- Provides us admin privileges to run some programs in Windows computer or server.
- Login into Windows server when we forget other user account password.
On the Windows server 2012 R2 logon screen, click the arrow on the left side of account image, and choose 'Other users'. Select default administrator, and type in default password to sign in to Windows server 2012 R2. And then you could reset Windows server 2012 R2 password with command or in Control Panel.
Also we could say that administrator in domain controller or PC has the highest privileges on server or computer, including but not only the privileges introduced above.
Related Articles:
We’ve talked previously about some of the features newly introduced with Windows Server 2012. In this article we’ll discuss Storage Spaces, a feature that allows you to provision storage to remove servers by creating storage pools. With Storage Spaces you can utilize physical inexpensive disks that once configured react just like a SAN (storage area network) device. In small enterprises that don’t require dedicated devices for storage space or high I/O operations, Storage Spaces provides a good alternative in achieving similar results.
To configure Storage Spaces you’ll need one or multiple unpartitioned physical disks (two for mirroring, three for mirroring with parity). Note that this technology offers support for SCSI, SATA, SAS and USB so it will suit you well for most configurations. Disks may be provided either externally or internally and can even be used in JBOD configuration. Storage spaces is a feature that will be installed by default on all Windows Server 2012 machines because it’s part of the File and Storage Services role, so you’ll not need to cover the installation part.
We’ll continue by installing and configuring a storage pool and then create a VHD that can be used by other machines. Note that in the context of SAN, a VHD is referred to as a LUN (Logical Unit Number). When talking about Storage Spaces we can use these terms interchangeably because they basically offer similar functionalities. Note that disks initialized for Storage Space will use the GPT partition style.
I’ve created a testing VM on my VirtualBox environment and I’ve attached two extra disks to be able to show you how to configure Storage Spaces.
Windows Storage Server 2012 Iso
Once you login on the machine, open the Server Manager console and navigate to the File and Storage Services/Storage Pools Section:
In the bottom right section of the window, you’ll see the physical disks attached on the machine. Note that in order to be able to create a storage pool, the disk must be at least 10 GB in size. All disks will be automatically added to the Primordial pool which contains all storage available on the server from which you can create storage pools. Use Ctrl to select multiple disks, right click and select Now Storage Pool or use the Tasks menu in the upper right corner of the panel. When the wizard starts, enter a name for the storage pool and then make sure that the desired disks are selected:
There are three options available in the allocation section:
- • Automatic – disk drives capacity is configured automatically
- • Hot Spare – the disk will not be part of the active pool, it will act as a replacement if one of the active disks fails. A hot spare will automatically be activated if one physical disk is not available anymore
- • Manual – the admin will configure manually the storage allocation
You can also use Powershell to configure Storage Pools much faster by using the New-StoragePool cmdlet just like in the following example:
Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard
New-StoragePool –FriendlyName MyNewPool –StorageSubsystemFriendlyName “Storage Spaces*” –PhysicalDisks (Get-PhysicalDisk PhysicalDisk1, PhysicalDisk2)
With the Get-StoragePool -IsPrimordial $true | Get-PhysicalDisk | Where-Object CanPool -eq $True you can get the physical disks available in the Primordial pool.
Once the storage pool has been created, we can create a virtual disk by right clicking on the pool and selecting New Virtual Disk:
Choose the storage pool that will host the VHD, set the name and description for your new VHD and set the provisioning method that you desire, there are three options available:
Windows Server 2012 Free Download
- • Simple
- • Mirror
- • Parity
If you want to find out more about SAN technologies available with Windows Server and more about provisioning method, check out this article.
In the provisioning tab select the type that suits best for your environment:
- •Thin – uses storage space from the pool as written on the VHD
- • Fixed – allocates all disk space from the beginning
All that’s left to do is to set the VHD size and finish the configuration. Once the VHD is ready, it will appear in the Virtual Disks section on the selected Storage Pool. Now you can use this VHD and allocate it to a server within your network:
That’s a about it for this article folks, as you can see, Storage Pools VHDs can be easily configured with Windows Server 2012 and really offers a fast and cheap solution to provide storage to your network servers. Because this feature is included in the Windows Server 2012 Edition by default, you only have to purchase the necessary license and physical disks rather than buy a SAN device thus seriously decreasing costs. Hope you’ve enjoyed this article and if so, please rate it in our dedicated section.
Dan Popescu
You can learn more about Dan Popescu by visiting him on Google+
